The air entering a turbocharged diesel engine is compressed before the fuel is injected, which is a significant difference between it and a traditional normally aspirated gasoline engine. Here, the turbocharger plays a crucial role in the diesel engine’s power output and efficiency.
The turbocharger’s function is to compress more air entering the engine’s cylinder. The oxygen molecules are squeezed closer together when air is compressed. With more air present, a normally aspirated engine of the same capacity can accommodate more fuel. As a result, the combustion process becomes more efficient overall and produces more mechanical power. Consequently, a turbocharged engine can have a smaller engine, which results in better packaging, benefits from weight reduction, and turbo is essential for this.
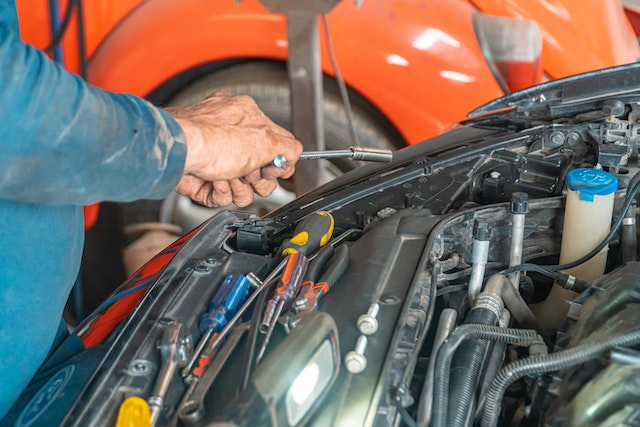

A turbocharger is a component added to an automobile’s engine to increase performance and increase overall efficiency. This is the rationale behind the widespread use of turbocharging by automakers. All the new vehicles are available with turbocharged engines, and more and more cars will be equipped with them over time.
A shaft connects the two sections that make up a turbo. The turbine that is attached to the other turbine that draws air in and compresses it into the engine is spun on one side by hot exhaust gases. Because more fuel can be burned when there is more air in the combustion chamber due to this compression, the engine has better power and efficiency.
In addition to providing more power, turbochargers are frequently referred to as free power devices because, unlike a supercharger, they are not powered by the engine. There is no loss of engine power because the turbocharger is powered by the hot, expanding gasses that come out of the engine. When traveling at higher altitudes, turbocharged engines are also not impacted the same way that naturally aspirated engines are. A normally aspirated engine finds it more difficult to obtain oxygen as it ascends higher in altitude due to the thinned atmosphere. By forcing oxygen into the engine’s combustion chamber, sometimes at a pressure double that of the environment, a turbocharger circumvents this issue.
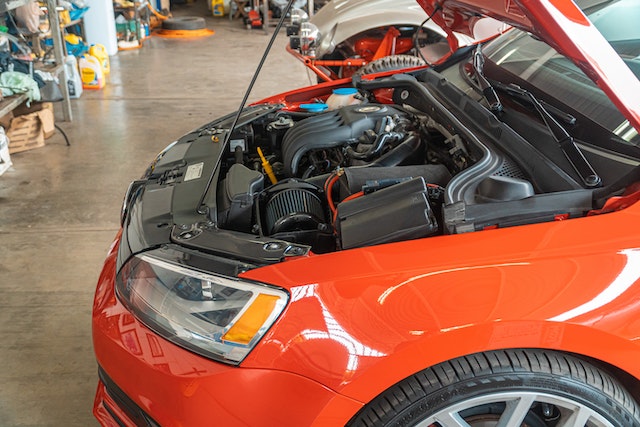

Although there is a misunderstanding about the relationship between turbocharged automobiles and fuel efficiency, turbochargers do help a vehicle’s fuel efficiency. It is not possible to increase fuel efficiency by adding a turbocharger to a normally aspirated engine. The process of downsizing an engine and then turbocharging it is how manufacturers increase fuel efficiency. The smaller, turbocharged engine would still have the same performance numbers or maybe slightly better but it would consume less fuel due of its reduced displacement.
And what exactly is a turbocharger? By pumping more air into the combustion chamber, a turbocharger also known as a turbo improves an internal combustion engine’s efficiency and power production. Also pulsar turbos should be working properly.
Because the compressor can push more air and thus more fuel into the combustion chamber than atmospheric pressure alone, it can produce more power than a normally aspirated engine.